Basic of Blockchain
First of all, blockchain is not cryptocurrency though its primary applications where in cryptocurrency. Blockchain is more of a concept than a technology, its inception was from the concept of Accounting and Auditing (Ledger System, Logs or trail of data), Information technology (Information Systems, Information Portals), Security and Identity management (Cryptography), Mathematics (Hashing and Algorithm).
Definition
Blockchain is a decentralized computation and information sharing platform which enables multiple authoritative domains which do not trust each other to cooperate, coordinate and collaborate in a rational decision-making process.
Blockchain is a cryptography-based software technology which functions as a distributed ledger that is heavily secured due to its attributes of peer to peer verification and authentication. Leveraging this technology to apply it in real world situations where a secured record is required for transactions, documents or any other sensitive information will lead to higher productivity and security.
Blockchain System:
The Blockchain system’s task is to ensure that all these individual copies are consistent with each other, that the local copies which every node has are identical, and these copies are always updated based on the global information i.e., if this node wants to enter some information to this blockchain then such information will get updated to all the copy of the blockchain that every node possess. That is basically the architectural platform of blockchain which supports a strong consistency among the local replica local information that every node has.
Key Components of Blockchain
- Decentralized Computing
- Cryptography (hashing)
- Chronological Ledger
- User Access (restricted / unrestricted)
- Security
- Trust building tool (Consensus)
- Cooperate, coordinate and collaborate tool between Participants. (Protocol for Commitment)
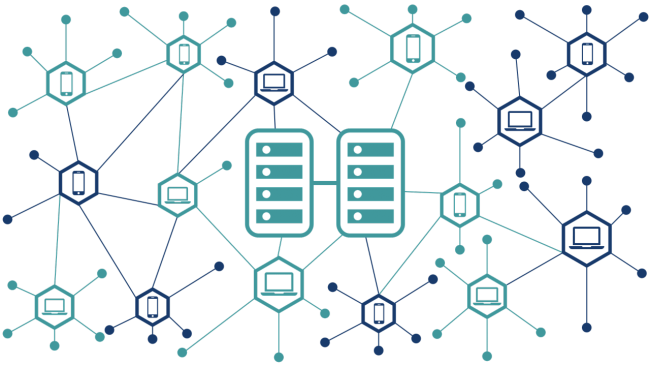
Decentralized and Distributed Network in blockchain
Centralized platforms are good, secured, but they are not scalable as well as they are not robust to failure. So, the move from a centralized architecture to a decentralized architecture or a distributed architecture is required.
Blockchain is a platform which helps you to support this kind of decentralized platform or a distributed platform where you can share the information among yourselves in a very custody manner.
Cryptography (hashing)
Cryptographically secured hash function is a function that map any sized data to a fixed size.For example, if you define hash function like H(x)=x%n, where x and n are integers and this % is the modular operation; that means, reminder after division by n. If we define a hash function like this way, that whatever be the value of x the value of H(x) will be in between 0 and n minus 1. This type of functions we call it a kind of hash function.
Hash function is a function that map any sized data to a fixed size. For example, if you define hash function like H(x)=x%n, where x and n are integers and this % is the modular operation; that means, reminder after division by n. If we define a hash function like this way, that whatever be the value of x the value of H(x) will be in between 0 and n minus 1. This type of functions we call it a kind of hash function.
Chronological Ledger
Transactions are “pseudo-anonymous”. Transactions are grouped together in “blocks”. Transactions are logged and stamped with information about the time, amount, and participants as if a notary is present at every transaction. Public ledger where every individual has their own copy of the global tractions which is synchronized and which is consistent and whenever a new transaction is made than the new transaction is validated against the old transactions that have already there inside the public ledger.
The public ledger which is available in an environment to everyone basically contained the information of all the transactions and the local copy of that environment’s entire public ledger is available to all the parties. The parties in the network by looking into their local public ledger will be able to understand that the particular transaction is valid or not valid.
User Access
The Information which is they’re in the blockchain belong to various parties and the copy of which is available to each and every party of the environment thus the Information is subject to privacy and authenticity restrictions. The focus is on data privacy and authenticity issues and Blockchain System should make every effort to understand those issues and proactively address any concerns.
Security
Security means, the data that is inserted in a public ledger or inside the blockchain is not tempered or false. The other nodes in the network should be able to understand that whatever this node is broadcasting is false information or that is the tempered information and they should be able to discard that particular information. That way the security need to be ensured because Distributed architecture do not have any “centralized authority” which is able to maintain the validity of the information to ensure the validity.
Protocol for commitment
The protocol for commitment means whenever someone is making a new transaction during that time it should be ensured that this particular transaction is valid, it will get committed to the existing public ledger or the existing blockchain otherwise not.
There should be a mechanism for validity checking of every upcoming transaction from the node and then based on that validity checking system is able to either accept the transaction & include it in the existing blockchain, or you can delete or discard the transaction.
Consensus
Consensus is an important aspect in the in the context of blockchain. In Blockchain there is a local copy of the information available to every individual party and there is no such central platform which maintains the consistency of the transactions or information. That is why the consensus mechanism ensures that whatever local copy every individual party has they are consistent with each other and everyone has the most updated copy and same is identical or similar to each other.
What is Blockchain Good For?
Blockchain is a solution which is looking for problems. Blockchain may be used for many things where there are many people involved and they don’t trust each other.
- Crypto currencies/Store of value – What is my account balance?
- Digital Identity – Who are you and how have you changed over time?
- Digital representation of a property/ Tokenization – Who owned this car over time?
- Tracking provenance of food or drugs – What country & postal code did this chicken come from?
In the real world the choice for the business leaders regarding the technology will not be clear, but the potential for the technology is immense. Companies need to proceed deliberately but cautiously, in the context of a through cost benefit analysis. There is no magic formula which fits all purpose.
Smart Contracts
A smart contract allows individuals to exchange data in a trusted, conflict-free manner without relying on a third party like a bank, lawyer or notary.
It is a self-automated computer program that can carry out the terms of any contract.
Mostly based on objective conditions precedent “If, then” criteria
Blockchain – Applications in Industries and Use Cases

Blockchain in Finance
- Payments and Remittance
Transactions can occur directly between two parties on a frictionless P2P basis. The technology’s application for overseas transactions has the potential to reduce risk, transaction costs and to improve speed, efficiency and transparency.
- Issuance, Ownership and Transfer of Financial Instruments
A blockchain-based securities market allows traders to buy or sell stocks directly on exchanges or directly to other market participants in a P2P manner without the intermediation services provide by a broker or clearing house.
- Clearing and Settlement Latency
On the blockchain, the entire lifecycle of a trade, including its execution, clearing and settlement can occur at trade level, lowering post-trade latency and reducing counterparty
Blockchain in Healthcare
- Cost Containment
The block chain can be filtered to identify and alert about specific activity on the chain, monitoring, using patterns, can include data that represents a doctor, consumer, drugs, procedures, all can to tokenized and added to the chain.
• Building a rule base using best practices, ICD codes, medical procedures and other costs can be monitored and audited using blockchain.
- Smart Contracts

Smart contracts would automatically pay providers when conditions of service are established such as:
• Validation that a service was received by a registered Medicaid patient
• Service was provided by a properly registered doctor & provider
• Neither party is on a known list of past participants in any fraud
Blockchain in Government
- Asset registration
A blockchain framework enables government agencies to increase the accuracy and efficiency of publicly held records by linking ownership of an asset to a single, shared ledger without disrupting existing registry data.
- Identity services
Blockchain enables government agencies to create a single, trustworthy collection of digital identity documents. These documents make it easier for government officials to reconcile data conflicts and provide citizens with control over their own identity.
- Fraud prevention and compliance
Blockchain creates a shared and trusted ledger that sequentially appends cryptographically secure data. The ledger is only accessible to trusted parties, giving government administrators the assurance that they’re working with data that’s up-to-date, accurate and nearly impossible to manipulate.
- Supply Chain
Blockchain makes the precise location of an object — and its accompanying digitized documentation — part of a traceable permanent record giving government full visibility of the supply chain.



Yo, ACB88bet! Gave it a shot last night. Pretty solid experience, gotta say. The slots were hitting, and I liked the variety of games. Definitely worth checking out if you’re looking for something new. Check them out: acb88bet!
Been using keo188bet for a while now, and honestly, I’m happy with it. The odds are decent and the site’s easy to navigate. Give it a try if you’re into that sort of thing. Link’s right here: keo188bet
This is a fantastic idle clicker with a surprisingly deep progression system! The constant stream of upgrades and new units keeps things engaging, and army of ages offers a satisfying sense of growth. If you love watching numbers go up and conquering endless waves, this is definitely for you!
Если требуется качественный результат, можно прогон хрумером заказать https://www.olx.ua/d/uk/obyavlenie/progon-hrumerom-dr-50-po-ahrefs-uvelichu-reyting-domena-IDXnHrG.html у специалистов.
Digital pharmacies are now integrated with telehealth platforms. Consumers browse medications online goldmed.info for convenience and accessibility. Professional consultations are usually available.
Думка спеціалістів особливо цінна на старті робіт. У статті ремонт квартир: поради експертів https://vseproremont.com/ подані перевірені рекомендації. Вони базуються на практичному досвіді.
Hello team!
I came across a 155 very cool page that I think you should dive into.
This resource is packed with a lot of useful information that you might find insightful.
It has everything you could possibly need, so be sure to give it a visit!
https://cryptomode.com/things-you-need-to-know-before-investing-in-cryptocurrency/
And remember not to forget, guys, — a person always may within the publication discover solutions to the most most tangled inquiries. Our team attempted to lay out the complete information using the most extremely easy-to-grasp way.